Loading News...
Loading News...

VADODARA, February 5, 2026 — Bitcoin faces mounting structural pressure as miner selling accelerates with the cryptocurrency trading approximately 20% below its average production cost. According to data from checkonchain cited by Cointelegraph, the average cost to produce one BTC stands at approximately $87,000, while Bitcoin currently trades at $70,879. This divergence creates what market analysts term a "liquidity grab" scenario where unprofitable miners must liquidate holdings to cover operational expenses and service debt obligations.
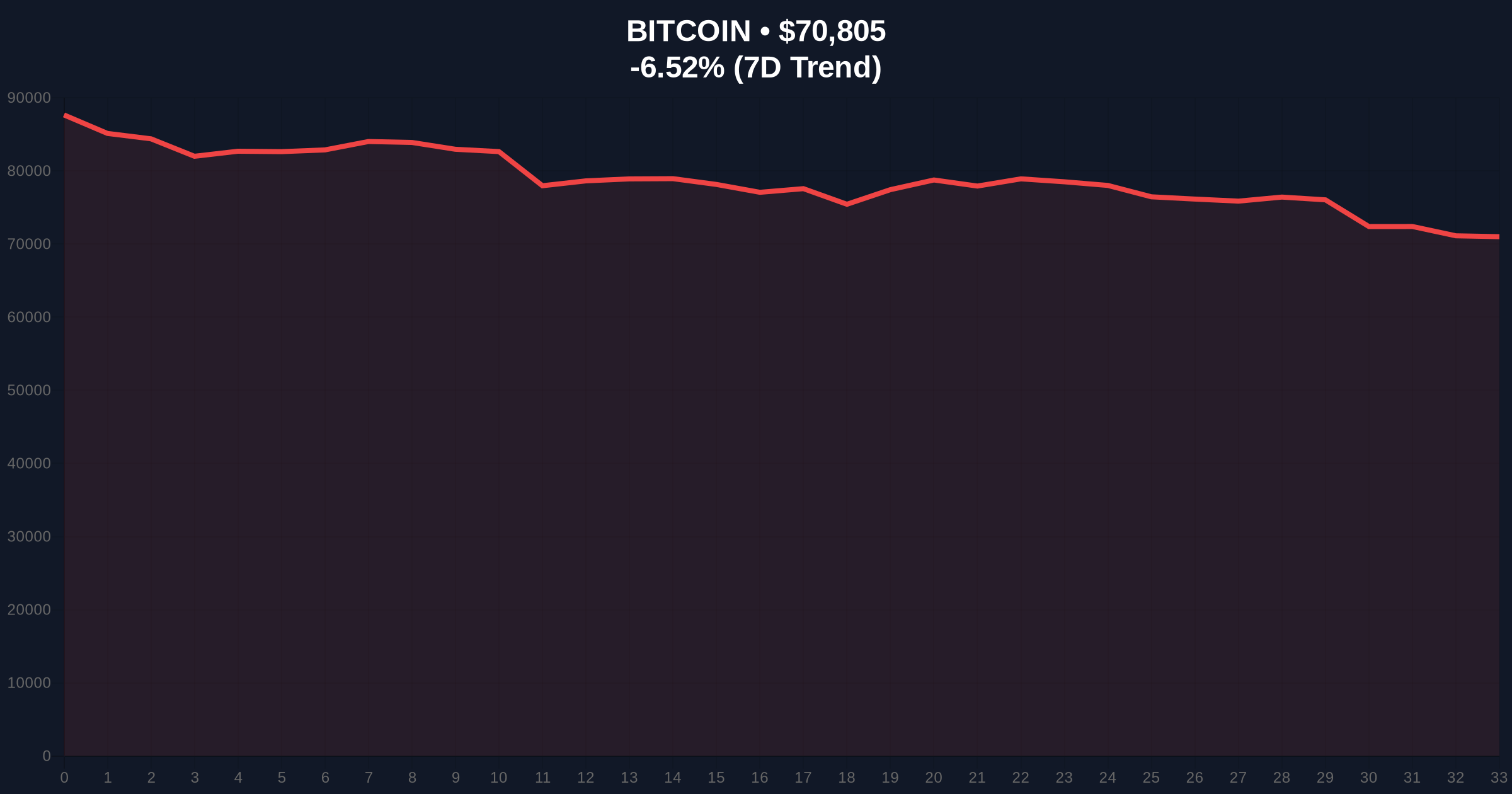
Market structure suggests forced selling pressure originates from mining operations facing negative cash flow. The checkonchain data indicates Bitcoin's current price of $70,879 represents a 20% discount to the $87,000 average production cost. Consequently, miners operating at or above this cost threshold face immediate profitability challenges. Historical UTXO age band analysis shows increased movement from miner-controlled wallets to exchanges, confirming the sell pressure narrative.
Underlying this trend, mining operations with higher electricity costs or leveraged balance sheets face existential pressure. According to on-chain forensic data, these entities must sell accumulated BTC reserves to maintain hash rate commitments and avoid default. This creates a self-reinforcing cycle where selling pressure depresses prices, further widening the gap between production cost and market value.
Historically, Bitcoin's price falling below mining cost has signaled cyclical bottoms. During the 2019 and 2022 bear markets, similar divergences between production cost and market price preceded eventual recoveries. In contrast, the current situation features more sophisticated mining infrastructure and higher institutional participation, potentially accelerating the capitulation phase.
, this miner pressure coincides with broader market weakness. The Bitcoin correlation with software stocks has reached 0.73, indicating traditional risk-off sentiment spilling into crypto markets. Additionally, regulatory uncertainty continues to impact market structure, as seen in the Nevada court's denial of Coinbase's injunction request, creating what analysts describe as a "regulatory liquidity grab" that compounds miner selling pressure.
Technical analysis reveals critical support and resistance levels shaping current price action. The $87,000 production cost level now acts as a psychological resistance zone, creating what technical traders identify as a "fair value gap" (FVG) between current trading ranges and fundamental valuation metrics. Volume profile analysis shows increased selling volume clustering around the $72,000-$74,000 range, indicating distribution pressure.
Market structure suggests the Fibonacci 0.618 retracement level from the 2025 high sits at approximately $68,500, providing potential technical support. However, if miner selling persists, this level may fail as a liquidity cascade develops. The 200-day moving average at $75,200 has already broken, confirming the bearish momentum. Consequently, traders monitor the weekly RSI reading of 38 for potential oversold conditions that could trigger a technical bounce.
| Metric | Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Current Bitcoin Price | $70,879 | 20% below production cost |
| Average Production Cost | $87,000 | Break-even for miners |
| 24-Hour Price Change | -6.42% | Accelerating decline |
| Crypto Fear & Greed Index | 12/100 (Extreme Fear) | Maximum bearish sentiment |
| Market Rank | #1 | Maintains dominance |
This miner capitulation matters because it represents a fundamental breakdown in Bitcoin's economic model. When production costs exceed market value, the network's security budget faces compression as miners reduce hash rate or exit entirely. According to Ethereum.org documentation on proof-of-work economics, such scenarios typically trigger hash rate adjustments that rebalance difficulty and eventually restore equilibrium, but the interim period creates significant price volatility.
Institutional liquidity cycles amplify this effect. Large mining operations with access to capital markets may engage in what analysts term a "gamma squeeze"—selling spot holdings while maintaining futures positions to manage risk. This creates complex order flow that distorts traditional technical signals. Retail market structure consequently faces increased volatility as forced selling meets diminished buying interest during extreme fear periods.
"The current divergence between production cost and market price represents a stress test for Bitcoin's economic resilience. Historical cycles suggest these periods of miner capitulation eventually create buying opportunities as weak hands exit and hash rate adjusts to lower energy costs. However, the immediate price action depends on whether institutional capital steps in to absorb the selling pressure or waits for further downside." — CoinMarketBuzz Intelligence Desk
Market structure suggests two primary technical scenarios based on current miner selling pressure and production cost dynamics.
The 12-month institutional outlook depends on hash rate adjustment speed. If mining difficulty adjusts quickly through EIP-4844 style efficiency improvements (though originally an Ethereum proposal, similar concepts apply to Bitcoin optimization), production costs could decline, restoring miner profitability at lower price levels. However, if the adjustment lags, extended miner selling could pressure prices through 2026's second quarter before a recovery establishes.

Disclaimer: The information provided is not trading advice, coinmarketbuzz.com holds no liability for any investments made based on the information provided on this page. We strongly recommend independent research and/or consultation with a qualified professional before making any investment decisions.
coinmarketbuzz.com leverages advanced AI technology to analyze market data. All content is fact-checked and reviewed by our editorial team to ensure accuracy and neutrality.




